MCP(Model Context Protocol): 是Anthropic于2024年11月推出的开放的模型上下文协议,标准化了应用向AI Agent提供上下文的方式,可以视作AI应用的USB-C接口,提供了一种将AI Agent连接到不同数据源和工具的标准化方式。
核心价值:
其核心价值在于:
- 协议化连接:标准化AI模型与外部系统的交互方式,将传统 $M×N$ 的集成度复杂度降为 $M+N$ 模式
- 生态构建:形成类似编程领域LSP(语言服务器协议)的开放生态,已有200+开源MCP服务器在GitHub涌现
- 性能突破:支持动态上下文管理,实测Token消耗降低40%,推理延迟控制在200ms内
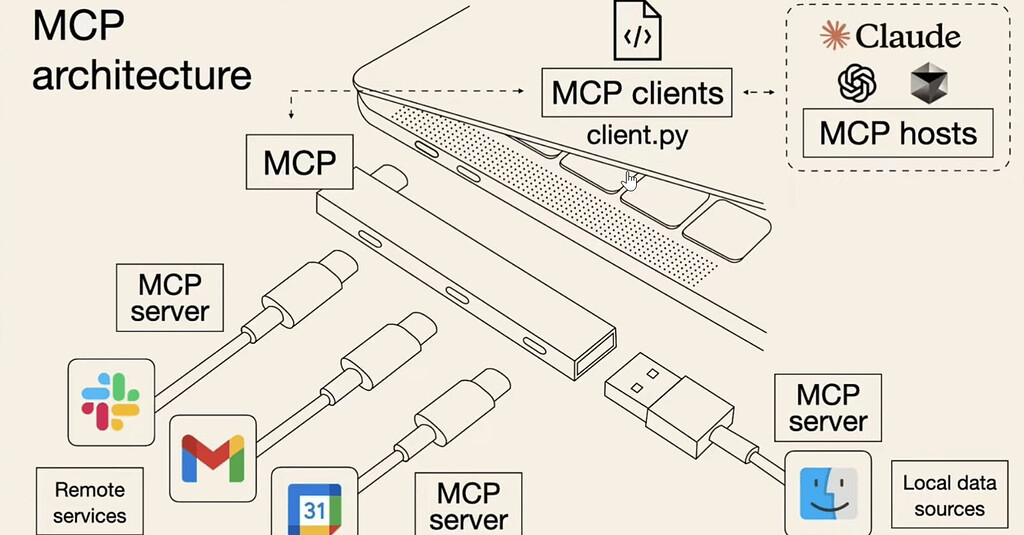
MCP遵循CS(Client-Server)架构,其中主机应用程序可以连接到多个服务器。
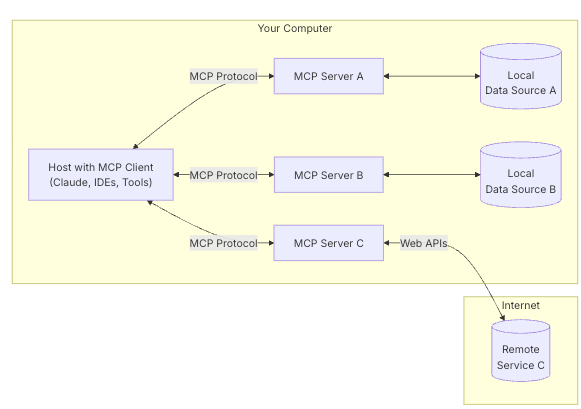
- MCP Hosts: MCP主机,表示希望通过MCP访问数据的程序,如Claude Desktop, AI Agent。主机通常会集成MCP客户端,客户端负责使用具体的MCP协议和服务器通信
- MCP Client: 与服务器保持 1:1 连接的协议客户端,是MCP协议的具体实现。它们充当了主机和服务器之间的桥梁,负责传递请求和响应。
- MCP Servers: 轻量级程序,每个程序都通过标准化模型上下文协议公开特定功能。- 一个服务器可以提供多个功能的集合,也可以专注于提供单个实用功能。
- Local Data Sources: 本地数据源,MCP 服务器可以安全访问的您的计算机文件、数据库和服务
- Remote Services: MCP 服务器可通过互联网(例如通过 API)连接到的外部系统。
Hello, MCP#
针对服务器开发For Server#
示例任务目标:实现一个能够进行天气预报和天气预警的服务器,包含get-forecast和get-alerts两个能力,并连接到MCP主机。
MCP服务器目前可以提供三种主要类型的功能:
- Resources: 资源,客户端可以读取的类似文件的数据(如API响应或文件内容)
- Tools: 工具, 可由LLM调用的函数(需经用户批准)
- Prompts: 提示词,预先编写的模板,帮助用户完成特定任务
这次任务主要关注在工具的部分。
- 环境准备:Python >= 3.10, Python MCP SDK >= 1.2.0
- 初始化项目环境和依赖安装
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| # Create a new directory for our project
uv init weather
cd weather
# Create virtual environment and activate it
uv venv
source .venv/bin/activate
# Install dependencies
uv add "mcp[cli]" httpx
# Create our server file
touch weather.py
|
- 初始化MCP实例
创建weather.py文件,导入MCP相关的包并创建对应的实例。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| from typing import Any
import httpx
from mcp.server.fastmcp import FastMCP
# Initialize FastMCP server
mcp = FastMCP("weather")
# Constants
NWS_API_BASE = "https://api.weather.gov"
USER_AGENT = "weather-app/1.0"
|
FastMCP类使用Python类型提示(type hints)和文档字符串(docstrings)自动生成工具定义,可以方便的创建和维护MCP工具。
- 完成工具开发
包含三个部分: (1) 辅助函数make_nws_request和format_alert来实现查询National Weather Service API以及数据格式化 (2) 工具执行处理器get-alerts和get-forecast (3) 执行server的main函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
| async def make_nws_request(url: str) -> dict[str, Any] | None:
"""Make a request to the NWS API with proper error handling."""
headers = {
"User-Agent": USER_AGENT,
"Accept": "application/geo+json"
}
async with httpx.AsyncClient() as client:
try:
response = await client.get(url, headers=headers, timeout=30.0)
response.raise_for_status()
return response.json()
except Exception:
return None
def format_alert(feature: dict) -> str:
"""Format an alert feature into a readable string."""
props = feature["properties"]
return f"""
Event: {props.get('event', 'Unknown')}
Area: {props.get('areaDesc', 'Unknown')}
Severity: {props.get('severity', 'Unknown')}
Description: {props.get('description', 'No description available')}
Instructions: {props.get('instruction', 'No specific instructions provided')}
"""
@mcp.tool()
async def get_alerts(state: str) -> str:
"""Get weather alerts for a US state.
Args:
state: Two-letter US state code (e.g. CA, NY)
"""
url = f"{NWS_API_BASE}/alerts/active/area/{state}"
data = await make_nws_request(url)
if not data or "features" not in data:
return "Unable to fetch alerts or no alerts found."
if not data["features"]:
return "No active alerts for this state."
alerts = [format_alert(feature) for feature in data["features"]]
return "\n---\n".join(alerts)
@mcp.tool()
async def get_forecast(latitude: float, longitude: float) -> str:
"""Get weather forecast for a location.
Args:
latitude: Latitude of the location
longitude: Longitude of the location
"""
# First get the forecast grid endpoint
points_url = f"{NWS_API_BASE}/points/{latitude},{longitude}"
points_data = await make_nws_request(points_url)
if not points_data:
return "Unable to fetch forecast data for this location."
# Get the forecast URL from the points response
forecast_url = points_data["properties"]["forecast"]
forecast_data = await make_nws_request(forecast_url)
if not forecast_data:
return "Unable to fetch detailed forecast."
# Format the periods into a readable forecast
periods = forecast_data["properties"]["periods"]
forecasts = []
for period in periods[:5]: # Only show next 5 periods
forecast = f"""
{period['name']}:
Temperature: {period['temperature']}°{period['temperatureUnit']}
Wind: {period['windSpeed']} {period['windDirection']}
Forecast: {period['detailedForecast']}
"""
forecasts.append(forecast)
return "\n---\n".join(forecasts)
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Initialize and run the server
mcp.run(transport='stdio')
|
- 启动MCP服务器: 调用命令
uv run weather.py
针对客户端开发For Client#
示例任务目标:构建一个可以连接到MCP Server的LLM助力的chatbot。
- 创建uv venv环境,安装依赖:
uv add mcp anthropic python-dotenv
MCP核心概念#
资源Resources#
资源是MCP向用户公开只读数据的方式,任何具有可读取内容的东西都可以是资源。
- Files on your computer: 计算机上的文件
- Database records: 数据库记录
- API responses: API 响应
- Application data: 应用程序数据
- System information: 系统信息
在MCP中每个资源都需要有:
- 唯一的 URI(例如
file:///example.txt或database://users/123) - 一个显示名称
- 可选的元数据,如描述,MIME类型等
- 内容: 文本或者二进制数据
借助资源,您可以以受控、标准化的方式向用户公开数据。例如一个文档服务器的资源:
1
2
3
| // Expose your company's documentation
"docs://api/reference" -> API documentation
"docs://guides/getting-started" -> User guides
|
技术细节#
通信方式SSE/STDIO/Streamable HTTP#
| 场景 | 推荐协议 | 一句话理由 |
|---|
| 本地脚本、桌面 IDE | stdio | 零网络、毫秒级延迟,本地插件首选 |
| 内网微服务、云函数 | Streamable HTTP | 双向流 + 断线续传,云时代的默认标准 |
| 老版本兼容、单向推送 | SSE | 简单但已标注 deprecated,了解即可 |
Stdio#
工作原理:
- 把 MCP Server 作为 子进程 启动
- 通过
stdin/stdout 传递标准的 JSON-RPC 2.0 报文 - 用
\n 字符分隔每一次完整的消息
使用场景:
- VS Code、Cursor、Cherry Studio 等本地 IDE 插件
- 离线环境、CI/CD 脚本、本地工具链
优点:
- 极简(一条命令就能运行)、低延迟、零网络配置
- 仅限本机、无法远程调用;子进程崩溃需要手动重启或处理
Streamable HTTP#
自 2025-03-26 起,官方已将 Streamable HTTP 设为 默认的远程传输协议。它解决了早期 SSE 的局限,是构建强大云端 MCP 服务的基石。
工作原理
- 客户端向服务器的
/mcp 端点发起 POST 请求,携带 JSON-RPC 消息 - 服务器接收请求后,立即返回 200 OK 或 202 Accepted 状态码
- 服务器在 同一个 HTTP 连接 中,通过 流式(Streaming) 的方式,可以多次发送响应(chunks),实现服务器向客户端的实时推送
- 客户端通过
Mcp-Session-Id 和 request_id 来匹配和处理异步返回的结果
关键特性
- 单一端点: 所有请求都通过
/mcp 处理,简洁明了 - 双向流支持: 兼容 HTTP/1.1 的chunked和 HTTP/2的Stream,实现高效的双向通信
- 断线续传与会话保持: 提升长连接场景下的稳定性。
- 标准鉴权: 可利用标准的HTTP Header进行身份验证和授权
SSE#
在 Streamable HTTP 成熟之前,SSE (Server-Sent Events) 是 MCP 支持的一种远程通信方式。它基于 HTTP,但只支持服务器向客户端的单向推送.
- Model Context Protocol
- MCP技术开发入门实战

